What is Sinusitis?
Many of us would have heard of someone around us who has a “sinus problem”. But is it really a sinus problem? Most people usually have chronic allergic rhinitis instead, producing the dreaded morning and night symptoms of sneezing, itching, nasal discharge or nasal congestion.
Sinuses are in fact air cavities located in the skull and communicating with the passages of the nose. They include the maxillary, frontal, ethmoidal, and sphenoid sinuses.
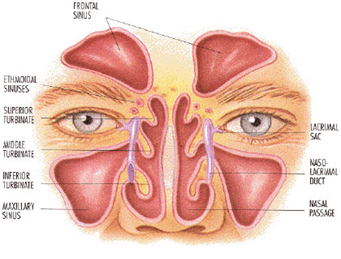
Sinusitis refers to the inflammation of the lining of the sinuses. This usually occurs as a complication of the common cold and is commonly viral in origin. Bacterial sinusitis is rarer, occurring in less than 10%, usually as a secondary post-viral infection. Acute sinusitis lasts less than 4 weeks, while chronic sinusitis can last longer than 3 months.
What are some of the symptoms of Acute Sinusitis?
Acute sinusitis usually causes these following symptoms after an episode of upper respiratory tract infection:
- Nasal congestion or blockage
- Nasal discharge that is thick and yellow to green
- Facial pain worse when bending forwards
- Others symptoms may include: fever, cough, inability to smell, toothache, ear pressure, fullness or hearing loss, headache, and bad breath.
When should I seek help for sinusitis?
Most patients improve within 7-10 days even without treatment, especially viral sinusitis.
Seek help if the above symptoms persist longer than 7-10 days.
Other red flags which warrant urgent medical attention include:
- High fever
- Sudden, severe pain in the face or head
- Swelling, puffiness or redness around one or both eyes
- Double vision or loss of vision
- Confusion, drowsy
- Neck stiffness
A full history and physical examination of the ear, nose, and throat would be required. Direct visualisation of the nasal passages and the sinuses with flexible endoscopy is usually required. Bacterial swabs may be required if there is inadequate response to antibiotics.In rare cases, other imaging techniques such as CT scans will be necessary to exclude complications.
What are the treatment options for Acute Sinusitis?
Unless there is clear evidence of a severe bacterial infection, initial treatment is symptomatic.
This includes a combination of:
- Pain relief medications
- Nasal saline irrigation
- Nasal decongestants (temporary)
Oral antibiotics may be necessary if symptoms persist for more than 7-10 days or if there are severe symptoms. Nasal steroid sprays may also be prescribed to reduce swelling of the lining of the nasal cavity and sinuses. This may be continued long term if there is evidence of allergic rhinitis.
What are some of the symptoms of Chronic Rhinosinusitis?
Persistence of the following for more than 3 months despite medical therapy:
- Thick and yellow to green nasal discharge or phlegm
- Nasal congestion or obstruction
- Facial pain or fullness
- Decreased sense of smell
Combination medical therapy include nasal saline washes, topical and systemic steroids, antibiotics, and antileukotriene agents.
Surgery in the form of Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) may be required for failed medical therapy or to correct structural anomalies. New technologies such as image guidance surgery (IGS), microdebriders, and balloon sinuplasty help to effectively treat chronic sinusitis and even nasal polyps, while minimizing pain and complications.
Please contact us if you have enquiries on Nose and Sinus Infections,
or request an appointment to see our ENT specialist.
